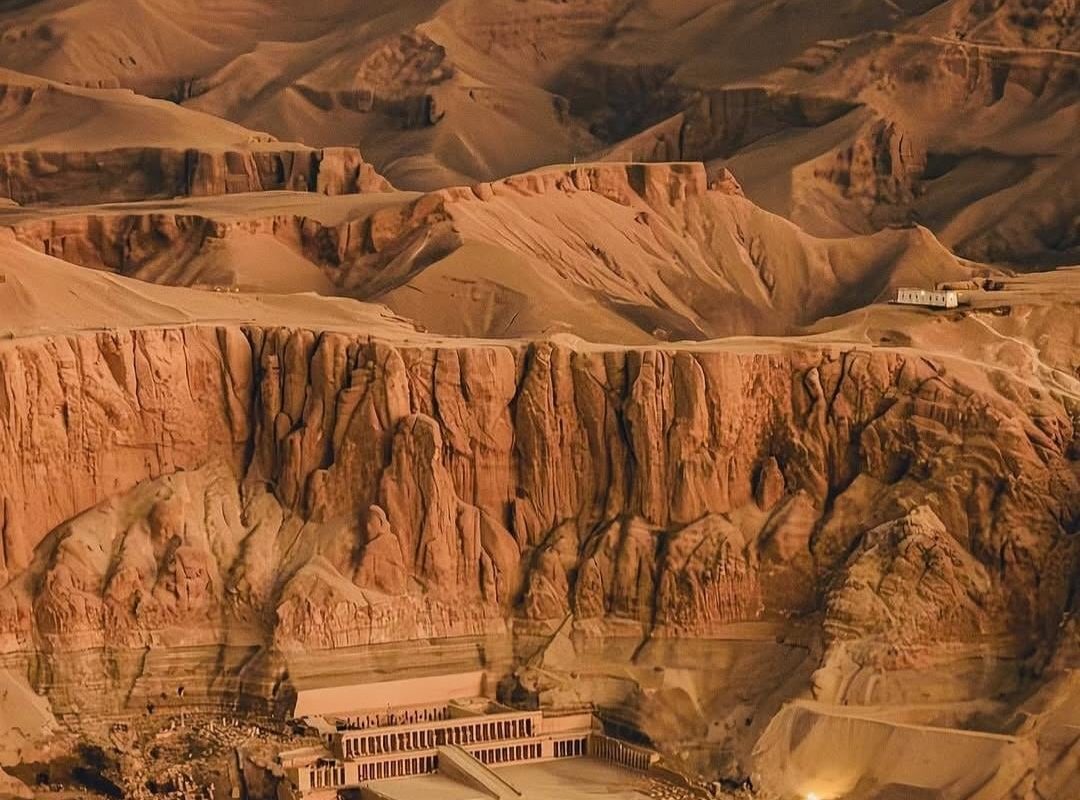
Deir el-Bahari Temple
Title: Deir el-Bahari Temple: Egypt’s Architectural Marvel of the Pharaohs
Meta Description: Discover the stunning Deir el-Bahari Temple, a masterpiece of ancient Egyptian architecture. Explore its history, design, and cultural significance in this comprehensive guide.
Deir el-Bahari Temple: Egypt’s Architectural Jewel
Introduction
Nestled on the west bank of the Nile, opposite modern-day Luxor, Deir el-Bahari stands as one of Egypt’s most breathtaking archaeological wonders. This UNESCO World Heritage Site is home to three magnificent temples, including the iconic mortuary temple of Queen Hatshepsut. A marvel of ancient engineering and artistry, Deir el-Bahari fuses natural landscapes with human ingenuity, offering visitors a window into the grandeur of the New Kingdom era.
A Glimpse into Ancient Majesty: What is Deir el-Bahari?
Deir el-Bahari (Arabic for “Northern Monastery”) is a complex of mortuary temples dating back to Egypt’s 18th and 19th Dynasties (c. 1550–1070 BCE). Carved into towering limestone cliffs, these structures served as sacred spaces to honor pharaohs and reunite them with the gods in the afterlife. The site’s three primary temples are:
- The Temple of Mentuhotep II: Built by the pharaoh who reunified Egypt after the First Intermediate Period.
- The Temple of Hatshepsut: The crown jewel of Deir el-Bahari, commissioned by Egypt’s most powerful female pharaoh.
- The Temple of Thutmose III: A smaller but historically significant sanctuary adjacent to Hatshepsut’s structure.
Historical Context: Why Was Deir el-Bahari Built?
Deir el-Bahari sits within the Theban Necropolis, a burial ground for pharaohs and nobles close to the Valley of the Kings. This strategic location was chosen for both its spiritual symbolism (the west bank represented the realm of the dead) and its dramatic natural amphitheater-shaped cliffs. The temples served dual purposes:
- Mortuary Rituals: Priests performed daily offerings to sustain pharaohs’ souls in the afterlife.
- Religious Festivals: Sites like Hatshepsut’s temple hosted processions during events like the Beautiful Festival of the Valley.
Architectural Brilliance: Design & Engineering
The most celebrated structure, Hatshepsut’s Temple, exemplifies innovation:
- Terraced Design: Three ascending colonnaded terraces mirror the surrounding cliffs, creating harmony between nature and architecture.
- Ramps and Colonnades: Central ramps connect levels, flanked by vibrant murals and Osiride statues of Hatshepsut.
- Sacred Alignments: The temple axis aligns with Karnak Temple across the Nile and the tomb of Hatshepsut in the Valley of the Kings.
Key Features Inside the Temple:
- Punt Reliefs: Detailed carvings depict Hatshepsut’s legendary expedition to Punt (modern-day Somalia), showcasing exotic goods like myrrh trees and ivory.
- Chapel of Hathor: Dedicated to the goddess of motherhood, adorned with cow-eared pillars and celestial imagery.
- Birth Colonnade: Illustrations legitimize Hatshepsut’s divine right to rule, showing the god Amun as her father.
Deir el-Bahari Through the Ages
- Decline: After Hatshepsut’s death, her successor Thutmose III defaced many of her monuments. Later, Coptic Christians repurposed parts as a monastery (hence “Deir el-Bahari”).
- Rediscovery: Excavations began in the 19th century, with Polish archaeologists restoring Hatshepsut’s temple to its former glory.
- Modern Significance: Today, it’s a testament to ancient Egypt’s architectural prowess and Hatshepsut’s groundbreaking reign.
Visiting Deir el-Bahari: Tips & Highlights
- When to Go: Visit early morning or late afternoon to avoid crowds and extreme heat.
- Combine with Nearby Sites: Pair your trip with the Valley of the Kings or the Temple of Karnak.
- Must-See Highlights:
- Hatshepsut’s Lower Courtyard: Sphinx-lined pathways and lush gardens (recreated).
- Upper Sanctuary: The holy-of-holies, originally housing statues of gods and Hatshepsut.
- Mentuhotep II’s Ruins: Foundations of Egypt’s first pyramid-style tomb complex.
- Guides & Photography: Hire a local Egyptologist for stories behind the reliefs. Photography is permitted, but drone use is prohibited.
Final Thoughts: Why Deir el-Bahari Endures
Deir el-Bahari Temple encapsulates the ambition, spirituality, and artistry of ancient Egypt. From Hatshepsut’s bold political statements etched in stone to the awe-inspiring fusion of cliffs and colonnades, it remains a pilgrimage site for historians, architects, and travelers alike. As restoration efforts continue, Deir el-Bahari stands resilient—a monument to humanity’s timeless quest for immortality.
Alt Text for Images (SEO Optimization):
- Image 1: “Deir el-Bahari Temple, Egypt – Terraced sanctuary against desert cliffs.”
- Image 2: “Hatshepsut Temple reliefs depicting expedition to Punt.”
- Image 3: “View of colonnades and ramps at Deir el-Bahari archaeological site.”
Keywords: Deir el-Bahari Temple, Hatshepsut Temple Egypt, ancient Egyptian temples, Luxor archaeological sites, mortuary temples, UNESCO World Heritage Egypt.
Craft a journey through history with this guide to Deir el-Bahari—a masterpiece carved in stone and time. 🌄📜