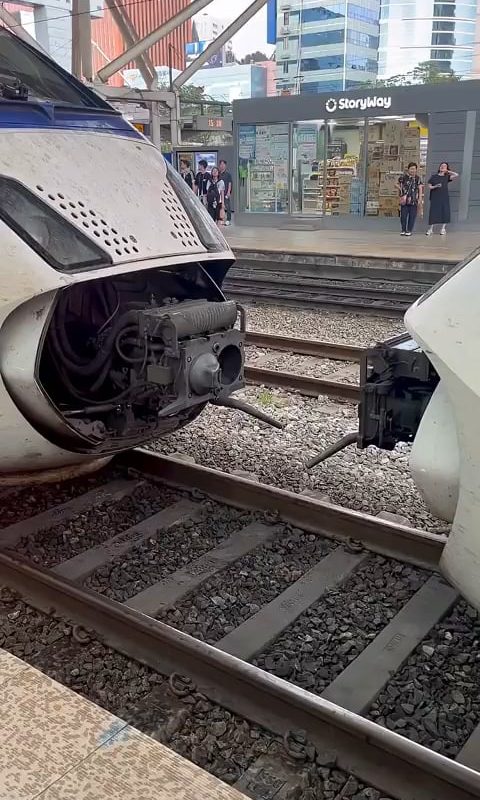
Rail Cars Coupling
The Essential Guide to Rail Cars Coupling: Types, Process, and Safety
Rail cars coupling is a fundamental process in rail transportation, ensuring the safe and efficient connection of locomotives, freight cars, and passenger coaches. This system not only allows trains to operate as cohesive units but also plays a critical role in safety, load distribution, and operational flexibility. In this guide, we explore the mechanics, types, and innovations in rail coupling technology that keep the global rail industry moving.
What Is Rail Cars Coupling?
Rail cars coupling refers to the mechanical systems used to link individual rail vehicles together, forming a train. These connections must withstand immense forces—like acceleration, braking, and shifting cargo weight—while enabling smooth movement. Historically, coupling was a manual process fraught with risk, but today’s automatic systems have revolutionized safety and efficiency.
Types of Rail Car Couplers
Different coupler designs serve specific applications based on factors like load capacity, geography, and train type. The most widely used systems include:
1. Janney Coupler (AAR Type E / Knuckle Coupler)
- Usage: Standard in North America for freight and passenger trains.
- Design: Features an interlocking “knuckle” that locks automatically when cars collide.
- Advantages: High strength, automatic engagement, and improved safety over manual systems.
2. Scharfenberg Coupler
- Usage: Common in Europe and high-speed passenger trains (e.g., metros, trams).
- Design: A streamlined, fully automatic coupler that connects pneumatic, electrical, and data lines.
- Advantages: Allows for tight coupling, reducing slack and improving ride comfort.
3. European Standard Coupler (Screw Coupler)
- Usage: Older or regional European freight networks.
- Design: A manual system using chains, hooks, and screw mechanisms.
- Drawbacks: Labor-intensive, higher derailment risk.
4. SA3 Coupler
- Usage: Popular in Russia and former Soviet states.
- Design: Semi-automatic, vertically interlocking system.
How Rail Cars Coupling Works
Modern automatic coupling simplifies what was once a dangerous manual task:
Step-by-Step Coupling Process
- Alignment: Cars are positioned so couplers align horizontally.
- Impact: As cars move toward each other, the coupler heads (knuckles) collide.
- Locking: The impact forces the knuckles to swing into a locked position, secured by pins or springs.
- Testing: Crews verify the connection’s integrity before departure.
For manual systems, workers physically link chains/hooks and tighten screw mechanisms—a process still used in legacy operations but phased out due to safety risks.
Safety and Efficiency Benefits
Advancements in coupling technology have transformed rail safety:
- Reduced Injuries: Automatic couplers eliminated the need for workers to stand between cars during linking.
- Derailment Prevention: Secure locking mechanisms minimize unintended decoupling.
- Operational Efficiency: Faster connections/disconnections improve turnaround times in freight yards.
Challenges and Maintenance
Couplers endure extreme stress, making maintenance critical:
- Common Issues: Wear, cracks, misalignment, or failed locking mechanisms.
- Routine Checks: Inspections focus on structural integrity, lubrication, and corrosion.
- Innovations: Smart sensors now monitor coupler health in real-time, predicting failures before they occur.
Applications Across Rail Operations
- Freight Trains: Robust Janney couplers handle heavy loads (e.g., coal, oil).
- Passenger Rail: Scharfenberg couplers enable smooth, jerk-free rides.
- Specialized Uses: Tankers, hoppers, and intermodal cars use customized coupler variants.
Future Trends in Coupling Technology
The rail industry is embracing smarter, greener solutions:
- Digital Monitoring: IoT-enabled couplers track force, temperature, and wear.
- Virtual Coupling: AI and communication tech allow trains to run closer together without physical links, boosting capacity.
- Material Science: Lightweight composites reduce energy consumption while maintaining strength.
Conclusion
Rail cars coupling is a cornerstone of railway operations, balancing raw mechanical power with precision engineering. From the iconic Janney coupler to emerging digital systems, innovation continues to enhance safety and efficiency. As rail networks expand globally, reliable coupling systems remain essential to keeping goods and passengers moving smoothly.
By understanding the mechanics, types, and maintenance needs of rail couplers, operators can ensure safer, more sustainable transportation for decades to come.
Keywords for SEO: Rail cars coupling, train couplers, Janney coupler, Scharfenberg coupler, automatic coupling, rail safety, freight train coupling, coupler maintenance, railway technology, railcar connectors.
Meta Description: Discover how rail cars coupling works, explore coupler types like Janney and Scharfenberg, and learn why this technology is vital for rail safety and efficiency.