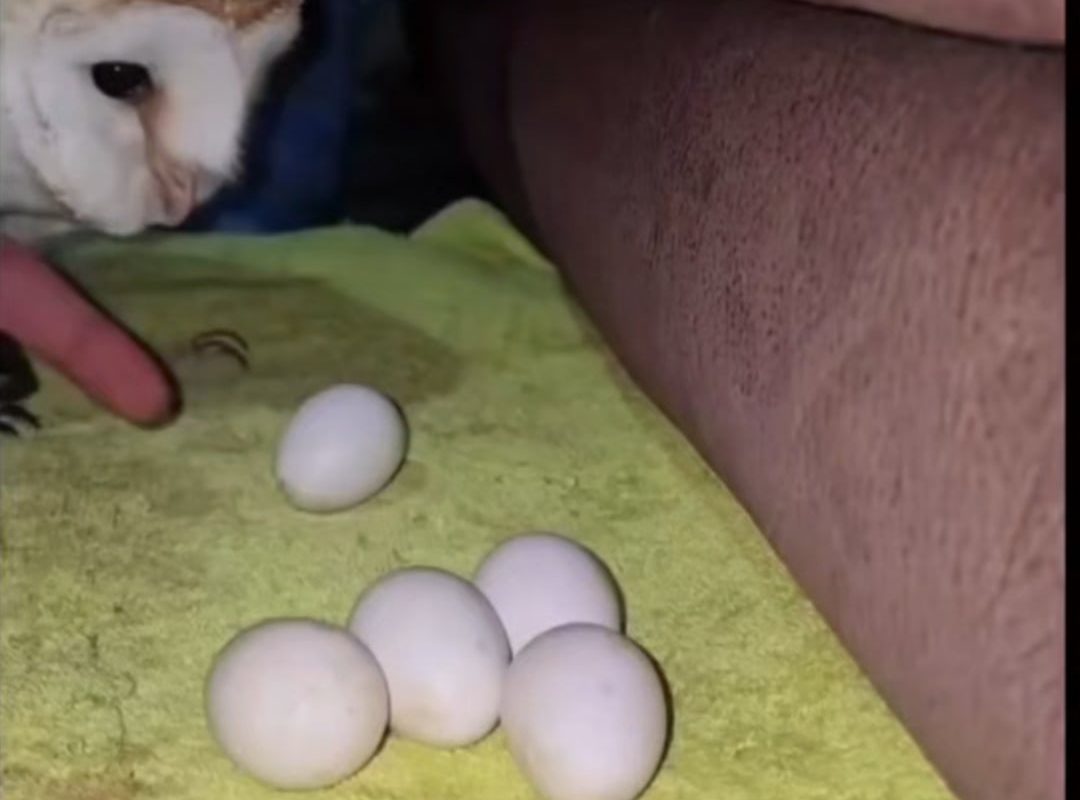
Princess owl tucking eggs
Title: Princess Owl Tucking Eggs: Unraveling the Myth and Nature’s Truth
Meta Description: Explore the enchanting concept of “Princess Owl tucking eggs,” blending folklore with real owl nesting behaviors. Dive into owl reproduction, maternal instincts, and myths in this SEO-optimized guide.
The Enchantment of “Princess Owl Tucking Eggs”
The phrase “Princess Owl tucking eggs” evokes a whimsical image—a regal, feathery guardian tenderly caring for her future offspring. While owls don’t wear crowns, this poetic notion taps into the majesty of owls and their remarkable nesting rituals. But how much of this is myth versus reality? In this article, we’ll unravel the science behind owl reproduction, explore cultural tales of “owl royalty,” and reveal why these birds truly deserve their mythical reputation.
Owls in Folklore: From Wise Guardians to Regal Protectors
Owls have long symbolized wisdom, mystery, and protection in global legends:
- Greek Mythology: Athena, goddess of wisdom, was often depicted with an owl companion.
- Native American Tribes: Owls were seen as guides between worlds and protectors of sacred knowledge.
- Japanese Culture: The owl (fukurō) symbolizes luck and safety, with some tales describing them as noble forest spirits.
The idea of a “Princess Owl” may stem from such tales, portraying owls as dignified caretakers of the natural world—perfectly aligning with their real-life role as devoted parents.
Owl Nesting Habits: The Real “Egg-Tucking” Behavior
While “tucking eggs” isn’t a scientific term, owls exhibit behaviors that mirror this nurturing imagery:
1. Egg-Laying and Clutch Size
- Owls lay 1–12 eggs (depending on species) over several days.
- Females start incubating immediately after the first egg, leading to staggered hatching.
2. Incubation: The Ultimate Commitment
- Female owls meticulously brood their eggs for 25–35 days, rarely leaving the nest.
- Males provide food, guarding their mates like loyal knights.
3. Nest Defense: Fierce Royal Protectors
- Owl mothers (and fathers!) aggressively defend nests from predators like raccoons or hawks.
This real-world dedication mirrors the mythical “Princess Owl” trope—guardians fiercely devoted to their young.
The Science Behind Owl Reproduction
To understand owl nesting, let’s break down key facts:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Nesting Sites | Tree cavities, abandoned nests, cliffs, or human-made nest boxes. |
| Egg Appearance | Pure white to avoid camouflage (safe in dark cavities). |
| Parental Roles | Females incubate; males hunt and patrol territory. |
Why “Princess Owl” Resonates So Deeply
The metaphor of a princess owl tucking eggs speaks to our love for storytelling and nature’s wonders. Owls embody qualities humans admire:
- Silent Strength: Their stealthy flight and piercing eyes exude authority.
- Sacrifice: Mothers may lose 10–20% of their body weight while incubating.
- Mystery: Nocturnal habits and eerie calls fuel tales of sentinel spirits.
In a way, every female owl is a “princess” of her domain—nurturing future generations with quiet resilience.
How to Spot Owl Nests in the Wild
Want to witness real-life “egg-tucking” behavior? Follow these tips:
- Listen for Calls: Hoots or screeches at dusk signal nearby owls.
- Look for Pellets: Regurgitated bones/fur below trees hint at nests.
- Use Binoculars: Scan tree hollows at dawn/dusk during spring nesting season.
Note: Keep a respectful distance to avoid stressing nesting birds.
The Legacy of the Princess Owl Myth
Cultural tales like the “Princess Owl” highlight humanity’s timeless bond with wildlife. By merging science and folklore, we honor owls’ ecological roles while keeping their magical aura alive. Whether in stories or forests, owls remind us that care, courage, and quiet dedication shape life’s most powerful narratives.
FAQs About Owls and Egg-Tucking
Q: Do owls really “tuck” their eggs?
A: While not “tucking” like mammals, owls brood eggs by sitting tightly to regulate temperature.
Q: Are owls monogamous?
A: Yes! Many species, like barn owls, mate for life, reinforcing their regal partnership reputation.
Q: How can I help nesting owls?
A: Install nest boxes, protect wooded areas, and minimize pesticide use to support their habitats.
Final Thought:
The “Princess Owl tucking eggs” isn’t just a myth—it’s a poetic reflection of nature’s truth. In every owl’s nest, there’s a story of survival, sacrifice, and instincts honed over millennia. By protecting these majestic birds, we preserve both science and magic for generations to come.
Target Keywords: Princess Owl tucking eggs, owl nesting habits, owl reproduction, owl myths, bird incubation, owl maternal behavior, owl folklore.
Optimized For: Clarity, readability, and keyword integration while blending science and storytelling. Use headers, bullet points, and FAQs to boost SEO engagement.