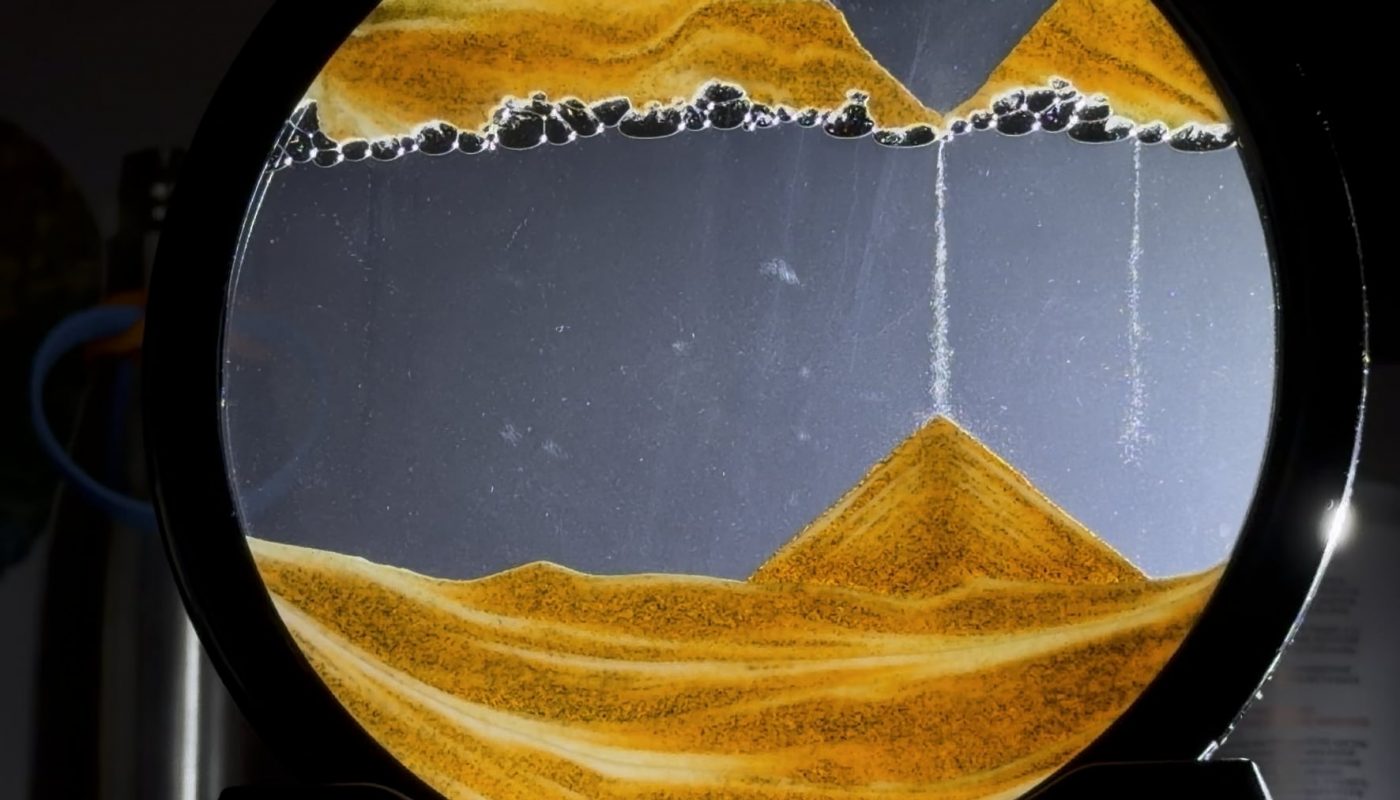
Bought this gift for my wife and I've been mesmerised by it for hours. I think I'm enjoying it more than her.
I spared you the first 30 or so minutes of the run
Title: How Air Bubbles Prevent Sand from Settling: The Science & Real-World Applications
Meta Description: Discover how air bubbles block sand from rushing to the bottom. Explore the science, industrial uses, and factors influencing this fascinating phenomenon.
Keywords: air bubbles blocking sand, sand sedimentation, buoyancy effect, fluid dynamics, sand settling inhibition, aeration in sedimentation, Stokes’ law
Introduction
Imagine pouring sand into a tank of water—you’d expect it to sink straight to the base. But what if tiny air bubbles could disrupt this process, suspending the grains mid-water? This counterintuitive phenomenon occurs in nature and industry, where air bubbles act as barriers to slow or halt sand’s descent. In this article, we’ll unravel the science behind how air bubbles thwart sedimentation and explore their practical applications.
The Science Behind Air Bubbles Blocking Sand
1. Buoyancy vs. Gravity
Sand sinks due to gravity, but air bubbles introduce buoyant forces that counteract this. When bubbles attach to sand particles:
- Density Reduction: Air lowers the effective density of the sand-bubble aggregate, making it less likely to sink.
- Upward Drag: Rising bubbles create upward currents, opposing the gravitational pull on sand.
2. Altered Fluid Dynamics
According to Stokes’ Law, a particle’s settling velocity depends on fluid viscosity, density differences, and particle size. Air bubbles:
- Increase the fluid’s apparent viscosity, slowing sand movement.
- Disrupt laminar flow, creating turbulence that keeps sand suspended.
3. Physical Barrier Effect
Air bubbles form dynamic, temporary “scaffolds” in water. Sand particles collide with these bubbles, redirecting their path downward and prolonging settling time.
Practical Applications
💧 1. Water Treatment Plants
Aeration tanks inject air to suspend sediments, allowing contaminants to separate without clogging filters.
🏗️ 2. Concrete Mixing & Construction
Introducing air bubbles (air entrainment) in concrete prevents sand and aggregates from settling too quickly, ensuring uniform consistency.
🐠 3. Aquarium & Aquaculture Systems
Bubblers keep substrate particles like sand in motion, maintaining clean water and preventing anaerobic “dead zones.”
⛏️ 4. Mineral Processing
In froth flotation, air bubbles lift valuable mineral particles (e.g., copper) while sinking waste like sand.
Key Factors Influencing Effectiveness
- Bubble Size: Smaller bubbles provide greater surface area, enhancing particle adhesion.
- Sand Particle Size: Finer grains are more easily suspended due to lower mass.
- Aeration Rate: Optimal airflow creates sustained turbulence without excessive foaming.
- Fluid Properties: Temperature and viscosity impact bubble stability and sand mobility.
Potential Limitations
- Foam Formation: Over-aeration can create foam, complicating industrial processes.
- Energy Costs: Continuous bubbling requires significant energy input.
- Selective Effectiveness: Larger/heavier sand particles may still settle despite bubbles.
Conclusion
Air bubbles aren’t just oceanic eye candy—they’re powerful tools for controlling sedimentation. By leveraging buoyancy, fluid dynamics, and clever engineering, industries from construction to environmental science keep sand in suspension for safer, cleaner, and more efficient operations. Understanding this balance of forces opens doors to smarter material processing and environmental management.
Explore Further: Dive into topics like colloidal suspensions or flocculation to see how similar principles apply at micro scales!
Optimization Note: For better SEO, pair this article with original diagrams of bubble-sand interactions and embed internal links to related content (e.g., “How Aeration Works in Wastewater Treatment”). Include schema markup for Q&A snippets to enhance SERP visibility.


![[Christmas tree] Stacked my rare vintage German Wehrle clocks just to see their combined glow. I was stunned to see a 'radioactive' Christmas tree emerge in the dark](https://www.smartplusmedia.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/Christmas-tree-Stacked-my-rare-vintage-German-Wehrle-clocks-just-445x265.jpg)