Australia is currently the hottest place on earth… by far
Title: Beyond the Boiling Point: Why Australia is Currently the Hottest Place on Earth by Far
Meta Description: Australia’s extreme heatwaves are shattering records, making it the hottest place on Earth. Discover why, where, and what this means for the planet.
Australia is the Hottest Place on Earth Right Now – Here’s Why
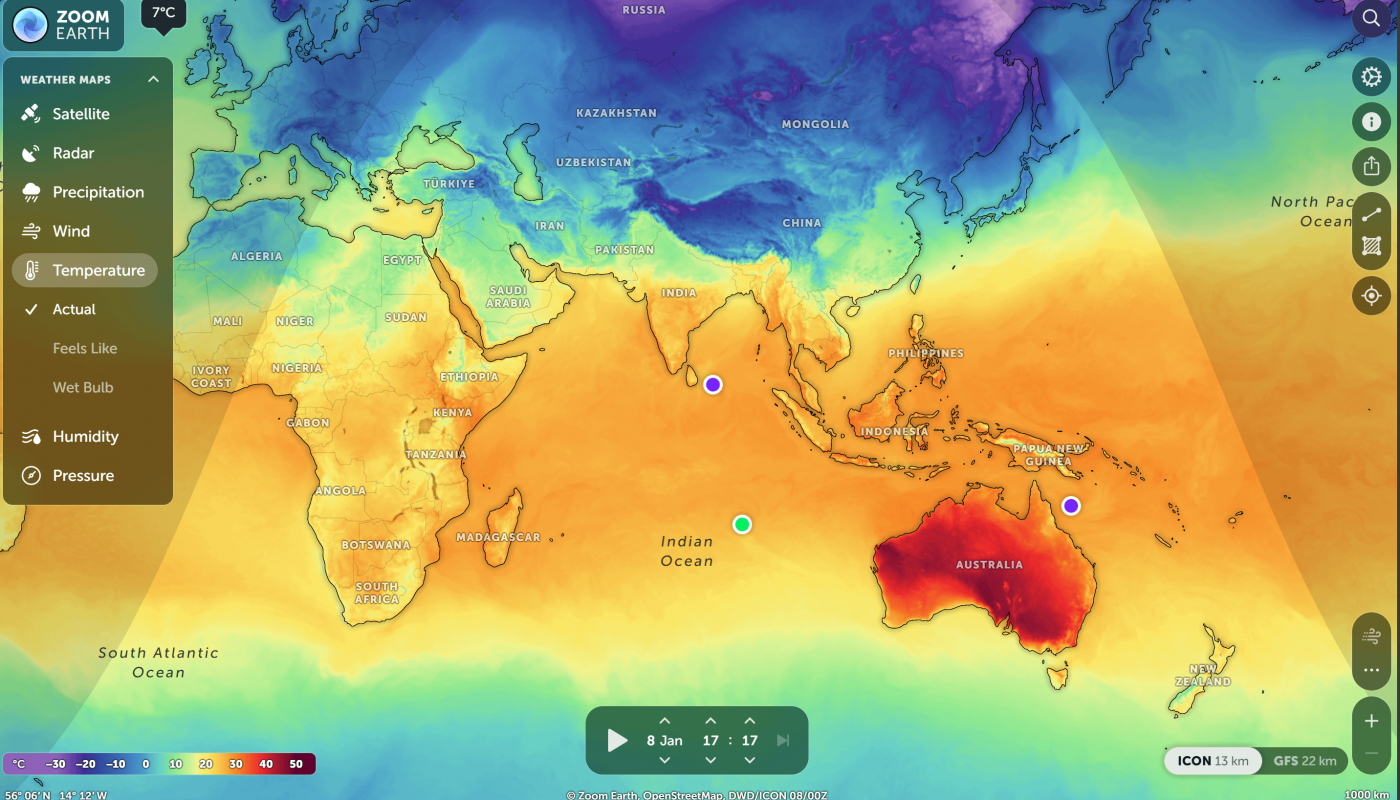
Australia is no stranger to scorching summers, but recent climate extremes have firmly cemented its place as the hottest spot on the planet—far surpassing other contenders like the Middle East or the Sahara Desert. With temperatures regularly exceeding 50°C (122°F) and vast swathes of the continent resembling a furnace, Australia’s heat isn’t just record-breaking—it’s rewriting the rules of extreme weather.
Here’s an in-depth look at why Australia is currently Earth’s hottest battleground, and what this means for the global climate crisis.
Record-Breaking Heat: Australia’s Scorching Reality
While deserts like Death Valley (USA) or Dasht-e Lut (Iran) often steal headlines, Australia’s recent heatwaves have made it the ultimate hotspot. Key milestones:
- Oodnadatta, South Australia: Hit 50.7°C (123.3°F) in 1960, still one of the highest temperatures ever recorded in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Onslow, Western Australia: Matched this record in January 2022, just months after vast wildfires ravaged the continent.
- The Outback: Average summer temperatures consistently exceed 45°C (113°F), with surface temperatures (measured by satellites) reaching a blistering 69.3°C (156.7°F) in 2022.
Australia’s climate isn’t just hot—it’s relentlessly extreme, with heat domes trapping air for weeks and nighttime lows failing to drop below 30°C (86°F).
Why Does Australia Get So Hot?
Five key factors turn Australia into a planetary oven:
-
Geography:
- A vast inland desert (the Outback) absorbs heat like concrete, radiating it back into the atmosphere.
- Minimal cloud cover and low humidity allow sunlight to pound the land unimpeded.
-
Subtropical High-Pressure Systems:
- Persistent high-pressure zones over central Australia act like a lid, trapping heat and blocking cooling rains.
-
El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO):
- El Niño phases amplify heat and drought, reducing rainfall and accelerating temperature spikes.
-
Climate Change Acceleration:
- Australia’s average temperature has risen 1.5°C since 1910, double the global rate. Heatwaves are now longer, hotter, and more frequent.
-
Urban Heat Islands:
- Cities like Sydney and Melbourne amplify temperatures by 5–10°C due to asphalt, vehicles, and air conditioning exhaust.
Impacts: When Extreme Heat Becomes a Crisis
Australia’s heat isn’t just uncomfortable—it’s deadly and economically catastrophic.
- Human Health: Heatstroke deaths have surged, particularly among outdoor workers and the elderly.
- Wildfires: The 2019-2020 “Black Summer” fires burned 24 million hectares, fueled by dry vegetation and 40°C+ temperatures.
- Wildlife Collapse: Koalas, kangaroos, and birds face dehydration and habitat loss at devastating scales.
- Infrastructure Meltdown: Roads buckle, rail lines warp, and power grids fail under extreme loads.
Australia’s Heat vs. the Rest of the World
| Location | Highest Recorded Temp (°C) | Key Difference |
|---|---|---|
| Death Valley (USA) | 56.7°C (134°F) | Drier, localized |
| Dasht-e Lut (Iran) | 70.7°C* (satellite) | Uninhabited desert |
| Australia (Outback) | 50.7°C (air) / 69.3°C (surface) | Affects major cities + ecosystems |
*Ground surface temperature, not air.
Australia stands out because its heat isn’t confined to remote deserts—it impacts coastal cities, farms, and globally unique ecosystems.
Climate Change: Fueling Australia’s Firestorm
Scientists agree: Australia’s extreme heat is a bellwether for planetary warming.
- Longer Heatwaves: The number of days over 40°C has doubled since 1970.
- Ocean Warming: Hot sea temperatures (like the 2023 marine heatwave) reduce coastal cooling.
- Feedback Loops: Heat dries soil, reducing moisture that would otherwise moderate temperatures.
“Australia is the canary in the coal mine,” says climatologist Dr. Joëlle Gergis. “What happens here foreshadows what other regions will face.”
Surviving the Heat: How Australians Adapt
From ancient Indigenous practices to modern tech, Australians are fighting back:
- Indigenous Wisdom: Aboriginal communities use “cool burn” fire management to reduce wildfire fuel.
- Architecture: Homes with reflective roofing, cross-ventilation, and shaded verandas.
- Policy: Heat action plans, public cooling centers, and workplace safety laws for extreme days.
Conclusion: A Stark Warning for the Planet
Australia’s status as Earth’s hottest place is more than a weather headline—it’s a dire signal of our climate future. While the nation adapts, its escalating heatwaves underscore a global truth: without aggressive emission cuts, 50°C days could become routine worldwide.
For now, Australia burns brighter than anywhere else—a blazing testament to the age of climate extremes.
Keywords for SEO:
Hottest place on Earth, Australia heatwave, Australian Outback temperatures, climate change Australia, extreme weather, hottest country, hottest continent, record-breaking heat, El Niño Australia.
Call to Action:
Stay informed about extreme weather trends—subscribe for climate updates and share this article to spread awareness!