How auroras are formed
Title: The Enigmatic Beauty of Auroras: A Deep Dive into How They Form
Meta Description: Discover how auroras form—nature’s mesmerizing light shows. Learn about the Sun’s role, Earth’s magnetic field, & the science behind the colors.
URL Slug: how-auroras-are-formed
How Auroras Are Formed: The Science Behind Earth’s Dazzling Light Shows
Auroras—known as the Northern Lights (Aurora Borealis) and Southern Lights (Aurora Australis)—are one of Earth’s most breathtaking natural phenomena. These shimmering curtains of green, pink, purple, and blue light dance across polar skies, captivating onlookers for millennia. But how are auroras formed? The answer lies in an otherworldly interplay between our Sun, Earth’s magnetic field, and the atmosphere.
The Solar Connection: Where It All Begins
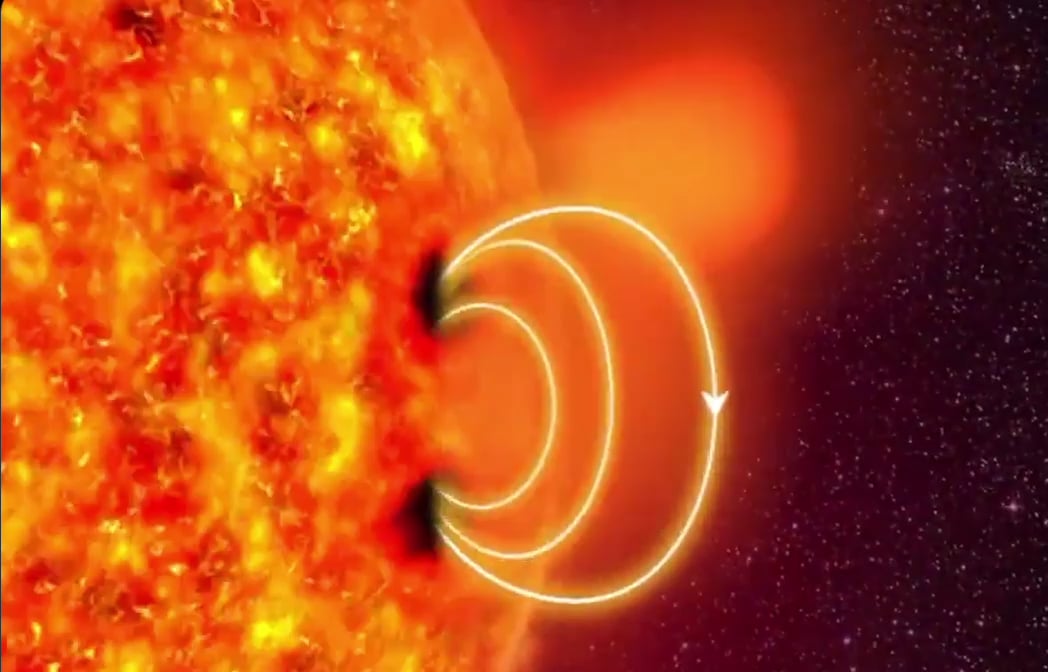
1. Solar Wind: The Sun’s Energetic Gift
- The process starts 93 million miles away on the Sun’s surface. During solar storms or coronal mass ejections (CMEs), the Sun releases streams of charged particles (mostly electrons and protons) into space in a flow called the solar wind.
- This solar wind travels at speeds of up to 1 million miles per hour, reaching Earth in roughly 1–3 days.
2. Earth’s Magnetic Shield: The Magnetosphere
- As the solar wind approaches Earth, it collides with our planet’s magnetic field, known as the magnetosphere. This invisible shield deflects most particles, funneling them toward the North and South Poles along magnetic field lines.
- Without the magnetosphere, these high-energy particles could strip away our atmosphere—making it essential for life.
The Aurora’s Birth: Energy Meets Atmosphere
3. Collision with Atmospheric Gases
At the poles, solar particles slam into gases in Earth’s upper atmosphere (the ionosphere, 60–200 miles above the surface), energizing oxygen and nitrogen atoms. Here’s what happens next:
- Electrons in atoms get “excited” and jump to higher energy levels.
- When they return to their normal state, they release energy as photons of light.
4. Why Different Colors? It’s All About Chemistry
- Green & Red: Caused by oxygen atoms. Green is the most common (collisions at ~60 miles altitude). Red appears higher up (~200 miles).
- Purple & Blue: Produced by nitrogen molecules at lower altitudes.
| Gas | Altitude | Color |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen | 60–150 miles | Green/Red |
| Nitrogen | Below 60 miles | Blue/Purple |
Where and When to Witness Auroras
The Auroral Ovals
Auroras typically occur in oval-shaped zones around the magnetic poles. During geomagnetic storms (triggered by intense solar activity), these ovals expand, making auroras visible at lower latitudes like the northern U.S., Canada, or Scotland.
Best Time to See Them
- Season: Dark, clear winter nights (September–April in the Arctic/Antarctic).
- Solar Cycle: Aurora frequency peaks every 11 years during the solar maximum (next peak: 2025).
Beyond Earth: Auroras in the Solar System
Auroras aren’t unique to Earth! Astronomers have observed them on:
- Jupiter & Saturn: Stronger than Earth’s due to powerful magnetic fields.
- Mars: Patchy auroras caused by solar particles hitting its weak magnetic pockets.
FAQs About Aurora Formation
Q: Can auroras occur during the day?
A: Yes, but sunlight makes them invisible. They’re best seen in darkness.
Q: Do auroras make sound?
A: Rarely. Some report crackling noises linked to electrical discharges, but this is debated.
Q: Are auroras dangerous?
A: No, but strong solar storms can disrupt satellites, GPS, and power grids.
Conclusion: A Cosmic Dance of Light
Auroras are the stunning result of charged particles from the Sun interacting with Earth’s magnetic field and atmosphere—a celestial ballet that highlights our planet’s connection to the wider universe. For travelers, scientists, and dreamers alike, witnessing an aurora is an unforgettable reminder of nature’s artistry.
Ready to see them? Head north to Iceland, Norway, or Alaska, or south to Tasmania or Antarctica during solar activity peaks. With a little luck and timing, you’ll catch the sky ablaze with color!
Optimized Keywords: How auroras form, Aurora Borealis explained, science behind northern lights, solar wind and auroras, aurora colors and causes, Earth magnetosphere aurora, when to see auroras.
Image Alt Text Suggestion: “Green and purple auroras dancing over snowy mountains under a starry sky.”
Internal Linking Suggestions:
- Link to “Best Places to See the Northern Lights”
- Link to “Solar Storms: Impact on Earth”
External Source Hint: NASA’s aurora research or real-time aurora forecasts.
By blending science with wonder, this SEO article answers user intent while enticing readers to explore Earth’s most magical light show. 🌌✨