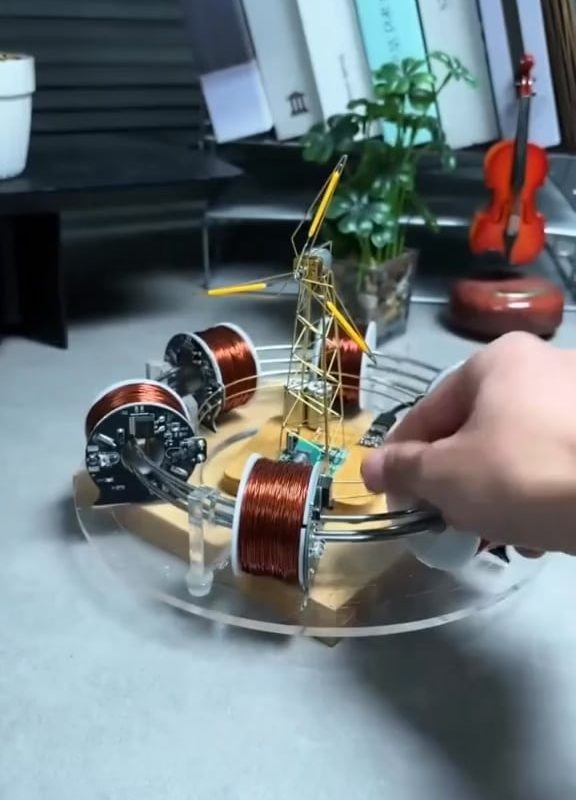
Magnetic motor powered by magnetic fields
Title: Magnetic Motors: The Future of Clean Energy or Perpetual Motion Myth?
Meta Description: Explore the science, potential, and controversy behind magnetic motors powered by magnetic fields. Can they deliver free energy, or do they defy physics? Learn the facts here.
Introduction
The idea of a magnetic motor powered solely by magnetic fields has captured imaginations for decades. Proponents claim it could revolutionize energy production by generating “free” electricity without fuel, emissions, or external power. But is this technology scientifically feasible, or is it a modern-day perpetual motion myth? This article dives into the science, promises, and challenges of magnetic motors—separating hype from reality.
What Is a Magnetic Motor?
A magnetic motor (or permanent magnet motor) is a hypothetical device designed to produce continuous motion—and thus usable energy—using the repulsive and attractive forces of permanent magnets arranged in a specific configuration. The concept relies on the principle that magnetic fields contain potential energy that could, in theory, power a rotor indefinitely without external input.
Key Components:
- Neodymium magnets: High-strength rare-earth magnets create intense magnetic fields.
- Rotor/Stator system: Magnets are positioned to create continuous rotation via magnetic repulsion and attraction.
- Energy output: The spinning rotor could theoretically drive a generator to produce electricity.
How Does a Magnetic Motor “Work”?
The proposed mechanism involves arranging magnets to create an unbalanced magnetic force, causing perpetual rotation:
- Like poles (N-N or S-S) repel, pushing the rotor away.
- Opposite poles (N-S) attract, pulling the rotor forward.
- Careful timing and shielding ensure the system never reaches equilibrium, sustaining motion.
But here’s the catch: Real-world factors like friction, air resistance, and energy dissipation mean no system can run indefinitely without an external energy source—a fundamental law of thermodynamics.
The Promise: Why Magnetic Motors Fascinate Innovators
1. “Free” and Clean Energy
Magnetic motors seemingly offer limitless power without fuel, solar, or wind, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and cutting carbon emissions.
2. Low Maintenance
With no combustion or moving parts (aside from the rotor), magnetic motors could operate silently and with minimal wear.
3. Off-Grid Potential
Ideal for remote areas or backup power, requiring only initial setup.
The Challenges: Why Science Is Skeptical
Despite decades of experimentation, no magnetic motor has ever passed rigorous scientific validation. Here’s why:
1. Violates Thermodynamics
The First Law of Thermodynamics states energy cannot be created or destroyed—only converted. Magnetic fields store energy, but extracting it requires work, and the system eventually loses energy to heat/friction.
2. No Verified Prototypes
Most “working” models online either hide external power sources or fail under controlled testing.
3. Energy Loss Is Inevitable
Even superconducting magnets experience resistance, eddy currents, and magnetic decay over time.
4. The “Perpetual Motion” Red Flag
Claims of machines requiring zero input energy are classified as perpetual motion machines—a scientific impossibility.
Notable Examples & Misconceptions
- Howard Johnson’s Magnet Motor (1979): Patented but never proven to work independently.
- YouTube “Free Energy” Devices: Often use concealed batteries or misleading editing.
- Maglev Trains & Industrial Motors: These use electromagnets powered by electricity, not permanent magnets alone.
Current Research & Legitimate Applications
While self-sustaining magnetic motors remain unviable, magnetic fields play critical roles in existing tech:
- Generators & Electric Motors: Convert mechanical energy to electricity (and vice versa) using electromagnets.
- Magnetic Levitation (Maglev): Uses electromagnetic propulsion for ultra-fast trains.
- NASA’s Ion Drives: Employ magnetic fields to accelerate ions in spacecraft.
Debunking Myths
Myth 1: “Magnets contain infinite energy.”
Fact: Magnets have finite energy stored in their aligned atomic dipoles. Once disrupted (e.g., by motion), the field weakens.
Myth 2: “Big Energy suppresses magnetic motor tech.”
Fact: If feasible, magnetic motors would disrupt the energy market—but no credible evidence exists to validate claims.
Conclusion: A Dream or Future Reality?
A magnetic motor powered purely by magnetic fields remains firmly in the realm of pseudoscience—for now. While innovation continues in magnetism (e.g., room-temperature superconductors), such a device would require rewriting the laws of physics. That said, research into magnetic technologies drives progress in renewables, transportation, and efficiency. Until then, the dream of “free energy” serves as a cautionary tale and a catalyst for genuine scientific discovery.
For now, the laws of physics remain undefeated.
Keywords for SEO:
Magnetic motor, permanent magnet motor, perpetual motion machine, free energy, magnetic fields, neodymium magnets, clean energy, Howard Johnson motor, thermodynamics, magnetic levitation.
Image Alt Tags:
- “Diagram of magnetic motor rotor and stator configuration”
- “Neodymium magnets arranged in a circular motor design”
- “Comparison of electric motor vs. hypothetical magnetic motor”
Internal Linking Opportunities:
- [How Do Electric Motors Work?]
- [The Science Behind Maglev Trains]
- [Renewable Energy Innovations to Watch]
Optimize your knowledge—share this article to spark informed debates about the future of energy! 🔄💡