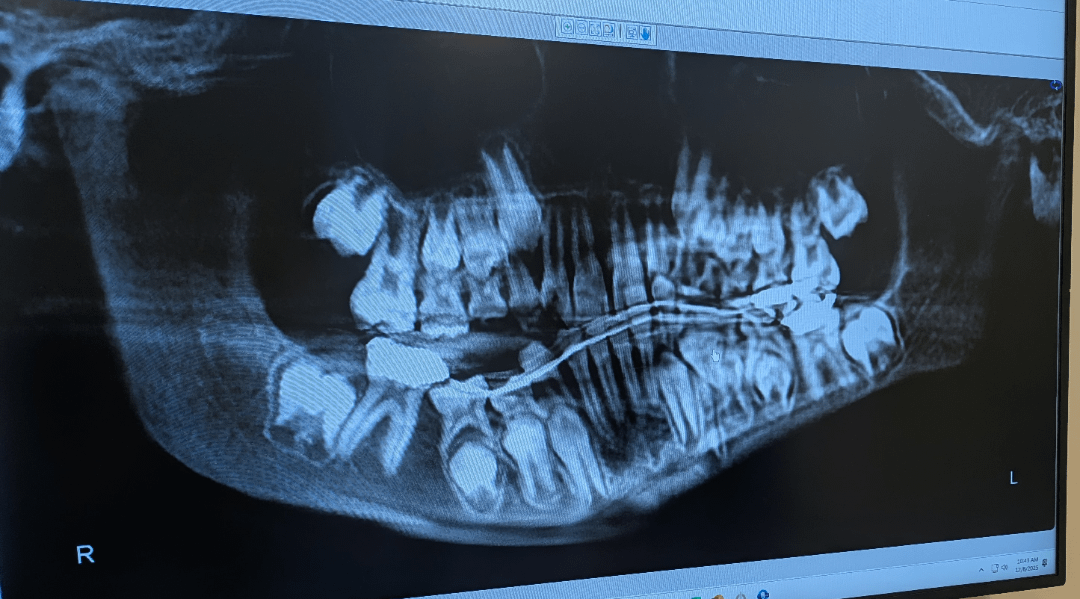
Most recent X-ray of my sons jaw
Title: Understanding Your Child’s Jaw Health: Insights from Their Most Recent X-Ray
Meta Description: Discover what a recent jaw X-ray reveals about your child’s oral health, common conditions detected, and how to interpret results for proactive care.
Introduction
If your child has recently undergone an X-ray of their jaw, you likely have questions about what the scan reveals, why it was necessary, and what comes next. Jaw X-rays are critical diagnostic tools for pediatric dentists and oral surgeons, providing a clear picture of bone structure, tooth development, and potential abnormalities. In this guide, we’ll break down what a recent jaw X-ray might indicate, common concerns detected, and how to collaborate with healthcare providers for your child’s long-term well-being.
Why Did My Child Need a Jaw X-Ray?
Jaw X-rays (or radiographs) are typically recommended to:
- Monitor Growth and Development: Track the alignment of adult teeth, jawbone structure, or asymmetries.
- Diagnose Trauma: Assess fractures or damage after injuries like falls or sports accidents.
- Identify Infections or Cysts: Detect abscesses, tumors, or cysts affecting teeth or bone.
- Plan Orthodontic Treatment: Guide braces, expanders, or surgical interventions.
- Investigate Pain or Swelling: Pinpoint causes of unexplained discomfort.
What the Latest X-Ray May Reveal
While only a dental professional can provide an accurate diagnosis, here’s what the most recent scan could show:
1. Tooth Development Issues
- Impacted Teeth: Adult teeth trapped beneath gums (common with wisdom teeth or canines).
- Delayed Eruption: Baby teeth blocking permanent teeth from emerging.
- Supernumerary Teeth: Extra teeth causing crowding or misalignment.
2. Bone Abnormalities
- Fractures: Hairline cracks from injuries.
- Osteopenia: Reduced bone density (rare in children).
- Cysts/Tumors: Fluid-filled sacs or growths requiring biopsy or removal.
3. Signs of Infection or Disease
- Abscesses: Pus-filled pockets near tooth roots.
- Periodontal Disease: Gum infection impacting bone (uncommon but possible in teens).
- TMJ Disorders: Jaw joint inflammation causing pain or limited movement.
4. Orthodontic Red Flags
- Malocclusion: Overbites, underbites, or crossbites.
- Crowding/Spacing Issues: Guides need for braces or expanders.
Preparing for the X-Ray: What Parents Should Know
- Safety First: Modern digital X-rays use minimal radiation—about the same as a short flight. Lead aprons protect other body parts.
- Ease Anxiety: Explain the process simply: “A camera takes pictures of your teeth to help the doctor.”
- Duration: Scans take 10–15 minutes; no pain is involved.
Interpreting Results: Next Steps
After the X-ray, your dentist or oral surgeon will discuss findings. Key questions to ask:
- What exactly did the X-ray reveal? Request a simplified explanation.
- Is this urgent or routine? Some issues (e.g., cysts) require swift action, while others need monitoring.
- What are our treatment options? From watchful waiting to surgery or orthodontics.
- How often should we repeat X-rays? Typically every 1–2 years unless complications arise.
Proactive Measures for Jaw Health
- Prevent Injuries: Use mouthguards for contact sports.
- Promote Oral Hygiene: Avoid cavities and gum disease with brushing/flossing.
- Balanced Diet: Calcium and vitamin D support bone strength.
- Regular Checkups: Early detection prevents minor issues from worsening.
FAQs About Pediatric Jaw X-Rays
Q: How soon can my child eat after an X-ray?
A: Immediately—no restrictions.
Q: Can infants/toddlers have jaw X-rays?
A: Yes, if medically necessary (e.g., birth trauma or genetic disorders).
Q: What if my child won’t stay still during the scan?
A: Clinics use padded stabilizers; sedation is rare but possible for intensive cases.
Q: Are 3D scans better than traditional X-rays?
A: Cone-beam CT scans provide 3D detail for complex cases but cost more.
Conclusion
A recent jaw X-ray is a vital step in safeguarding your child’s oral health. Whether it revealed a minor concern or a need for intervention, proactive collaboration with dental professionals ensures your son receives the best care. Remember: Early detection and treatment pave the way for a lifetime of healthy smiles.
Note: This article is for educational purposes only. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Keywords: Pediatric jaw X-ray, child oral health, interpreting X-ray results, impacted teeth, orthodontic planning, jaw fracture, pediatric dental care, TMJ disorders in kids.