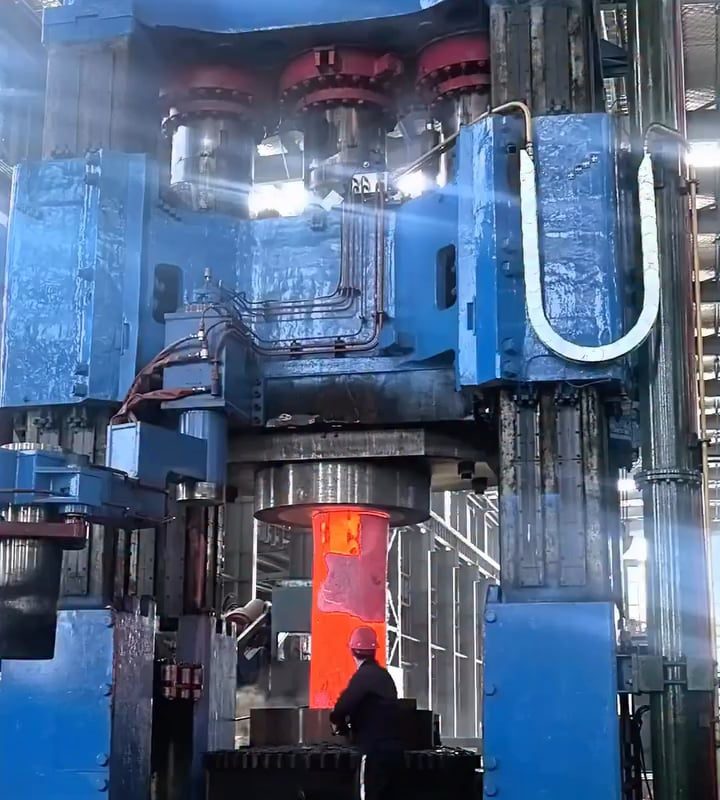
The precision forging hydraulic press used in heavy manufacturing and metallurgy to shape large, critical metal components.
Title: Precision Forging Hydraulic Presses: Powering Heavy Manufacturing & Metallurgy
Meta Description: Explore how precision forging hydraulic presses enable the production of critical, large-scale metal components for aerospace, automotive, and energy industries. Learn about their advantages and applications.
Introduction
In the world of heavy manufacturing and metallurgy, the ability to shape massive metal components with unparalleled accuracy is non-negotiable. From aerospace turbine blades to industrial crankshafts, these parts must meet rigorous standards for strength, durability, and dimensional precision. Enter the precision forging hydraulic press—a technological powerhouse revolutionizing how industries forge critical metal parts. This article dives into the mechanics, benefits, and applications of these advanced machines in modern manufacturing.
What is a Precision Forging Hydraulic Press?
A precision forging hydraulic press is a heavy-duty machine that uses pressurized fluid to deform metal blanks into near-net-shape components with exceptional dimensional accuracy. Unlike traditional mechanical hammers or screw presses, hydraulic presses deliver controlled, consistent force across large surface areas, making them ideal for shaping high-strength alloys, titanium, and superalloys used in critical applications.
How It Works:
- Closed-Die Forging Process: Metal is compressed within precision-engineered dies, ensuring minimal material waste and tight tolerances (±0.2mm).
- Hydraulic System: A pump generates fluid pressure, which drives pistons to apply forces ranging from 10,000 to 100,000+ tons.
- Advanced Control Systems: PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and sensors adjust speed, pressure, and stroke in real-time for repeatable results.
Key Features & Advantages
Precision forging hydraulic presses outperform traditional forging methods in demanding environments. Here’s why:
-
Superior Material Utilization
Near-net-shape forging reduces machining needs by up to 70%, slashing material waste in costly alloys like nickel-based superalloys. -
Enhanced Structural Integrity
Uniform grain flow and denser microstructures boost fatigue resistance—critical for components like landing gear or nuclear reactor parts. -
Scalability for Large Components
Handles massive parts (e.g., wind turbine shafts up to 15 meters long) with consistent force distribution. -
Flexibility & Adaptability
Adjustable pressure and stroke accommodate diverse materials, from aluminum to high-temperature steels. -
Energy Efficiency
Hydraulic systems consume power only during pressing, unlike continuously running mechanical presses.
Industries Relying on Precision Forging Presses
1. Aerospace & Defense
- Applications: Turbine disks, engine mounts, structural airframe components.
- Why Hydraulic Presses? Allows forging of heat-resistant titanium and Inconel at controlled temperatures to prevent defects.
2. Energy Sector
- Applications: Nuclear reactor vessel heads, wind turbine hubs, oil & gas valve bodies.
- Why Hydraulic Presses? Ensures reliability in extreme environments (high pressure, corrosion).
3. Automotive Manufacturing
- Applications: Transmission gears, crankshafts, EV battery housings.
- Why Hydraulic Presses? High-volume production with minimal post-forging machining.
4. Heavy Machinery
- Applications: Mining equipment axles, crane hooks, hydraulic cylinders.
- Why Hydraulic Presses? Delivers the force needed for ultra-high-strength steel components.
Technical Innovations Driving Precision
Modern hydraulic presses integrate cutting-edge technologies to push the boundaries of forging:
- IoT & Predictive Maintenance: Sensors monitor press health, predicting failures before downtime occurs.
- Closed-Loop Control: Compensates for variables like material temperature or die wear mid-cycle.
- Multi-Axis Capabilities: Some systems add lateral rams for complex geometries in a single heat cycle.
Challenges & Solutions
While precision forging presses are transformative, operators face hurdles:
- High Initial Investment: Solutions include modular designs for scalability and ROI-focused lifecycle management.
- Die Wear: Advanced coatings (e.g., ceramic or DLC) extend tooling life in high-temperature forging.
- Skilled Labor Shortage: AI-assisted controls simplify operation and reduce training needs.
The Future of Precision Forging
As Industry 4.0 reshapes manufacturing, hydraulic presses are evolving:
- Hybrid Presses: Combining hydraulic and electric drives for speed and energy savings.
- Additive Manufacturing Integration: 3D-printed die inserts enable rapid prototyping of complex parts.
- Sustainable Forging: Recycled alloys and presses powered by renewable energy reduce carbon footprints.
Conclusion
Precision forging hydraulic presses are the backbone of heavy manufacturing, enabling industries to produce stronger, lighter, and more reliable metal components. As demand grows for large-scale critical parts in renewable energy and advanced transportation, these machines will continue to drive innovation—merging raw power with digital precision to forge the future of metallurgy.
Keywords for SEO:
Precision forging hydraulic press, closed-die forging, heavy manufacturing, metallurgy, near-net-shape forging, hydraulic press advantages, aerospace forging, large metal components, industrial forging press.
CTA:
Interested in optimizing your forging process? Contact our experts to explore how precision hydraulic presses can elevate your production capabilities.