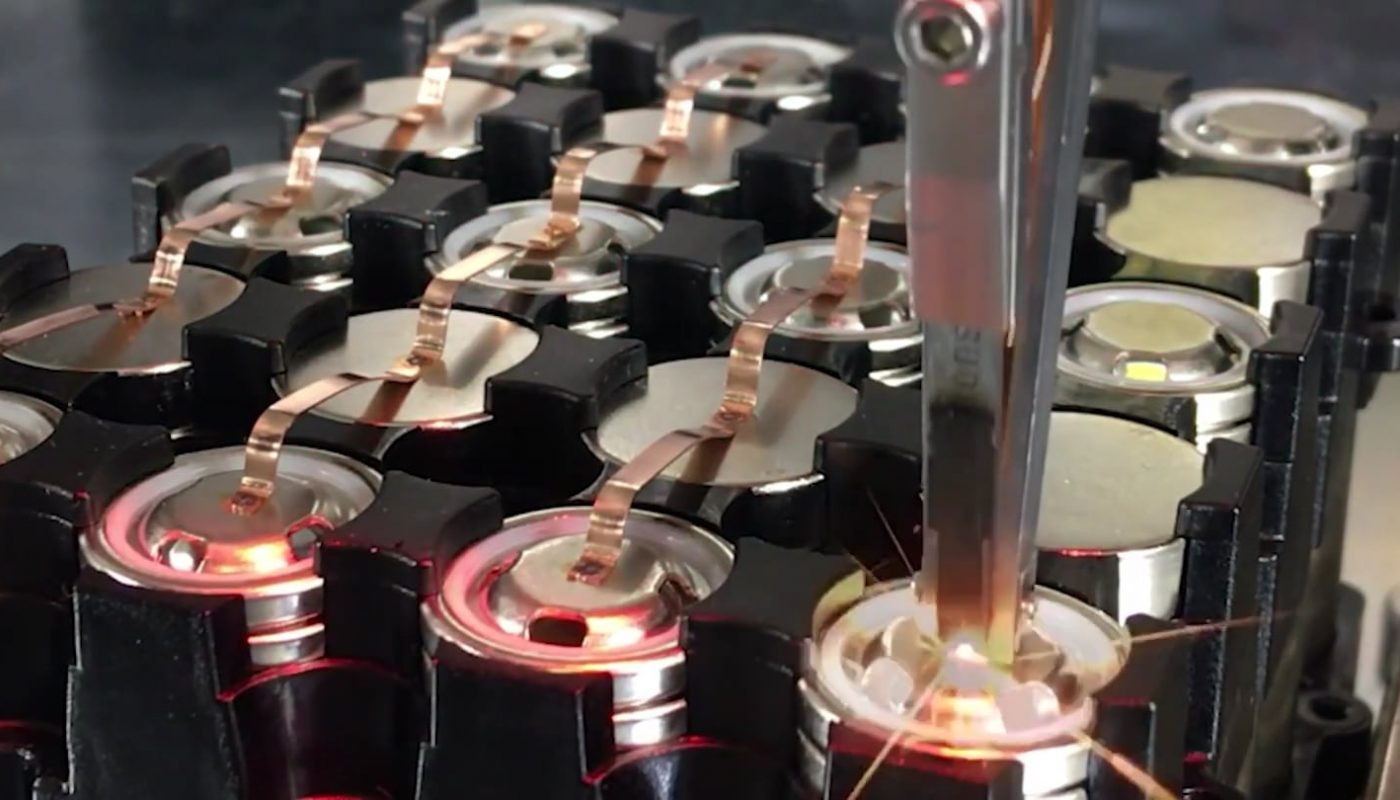
I think its Ultrasonic wire bonder machine ?
Title: Understanding Wire Bonding Machines: The Backbone of Semiconductor Packaging
Meta Description: Dive into the world of wire bonding machines, their functions, types, and applications in semiconductor manufacturing. Learn how they drive innovation in electronics.
Introduction
In the intricate ecosystem of semiconductor manufacturing, wire bonding machines play a pivotal role in ensuring the reliability and performance of integrated circuits (ICs). As demand for smaller, faster, and more powerful electronic devices grows, understanding the technology behind wire bonding becomes essential for engineers, manufacturers, and tech enthusiasts alike. In this guide, we’ll explore how wire bonding machines work, their key components, applications, and the latest innovations shaping the industry.
What Is a Wire Bonding Machine?
A wire bonding machine is an automated or semi-automated device used to create electrical interconnections between a semiconductor chip (die) and its package or substrate. This process involves bonding ultrathin wires—typically made of gold, aluminum, or copper—with diameters as small as 15–50µm (micrometers). These connections enable signals and power to flow between the chip and external circuits, forming the lifeline of modern electronics.
Key Components of a Wire Bonding Machine
-
Bond Head:
- Moves with precision to position wires between the die and substrate.
- Uses force, heat, and/or ultrasonic energy to form robust bonds.
-
Wire Spool & Feeding System:
- Supplies the bonding wire continuously from a spool to the bond head.
-
Optical System:
- High-resolution cameras and sensors align the bond head with micron-level accuracy.
-
Stage & Platform:
- Holds the semiconductor package in place during bonding.
-
Ultrasonic Generator or Thermo-Compression Tool:
- Applies energy (ultrasonic vibration or heat) to fuse wires onto contact pads.
-
Software Controls:
- Advanced algorithms manage speed, force, and placement consistency.
Types of Wire Bonding Technologies
There are three primary wire bonding techniques, each suited for specific applications:
1. Ball Bonding (Gold or Copper Wire)
- Process: A spark (Electronic Flame-Off) melts the wire tip to form a ball, welded to the chip pad using heat and ultrasonic energy.
- Applications: High-speed bonding for ICs, LEDs, and consumer electronics.
- Advantages: Fast process, high reliability, and fine-pitch capability.
2. Wedge Bonding (Aluminum or Gold Wire)
- Process: Uses ultrasonic energy to press a wedge-shaped wire end onto the pad.
- Applications: Sensitive devices (e.g., RF components), high-frequency bonding.
- Advantages: Lower bonding temperatures, ideal for temperature-sensitive materials.
3. Ribbon Bonding
- Process: Flat ribbons replace round wires for lower inductance and higher current capacity.
- Applications: Power semiconductors, aerospace, and automotive electronics.
Applications of Wire Bonding Machines
Wire bonding is ubiquitous in semiconductor packaging across industries:
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, laptops, and wearables.
- Automotive: ECUs, sensors, and electric vehicle battery management.
- Medical Devices: Implants, diagnostic equipment.
- Aerospace & Defense: High-reliability systems for extreme conditions.
Advantages of Modern Wire Bonding Machines
- Speed: Up to 30 bonds per second for mass production.
- Precision: Capable of sub-micron alignment accuracy.
- Flexibility: Compatible with various wire types and package designs.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Lower material waste compared to alternatives like flip-chip bonding.
Choosing the Right Wire Bonder: Key Considerations
- Wire Material: Gold (high conductivity) vs. copper (cost-effective, higher strength).
- Bonding Pitch: Machine accuracy to support fine-pitch (<40µm) bonding.
- Throughput: Speed requirements for high-volume production.
- Automation Level: Integration with SMART factories (Industry 4.0-ready systems).
Innovations in Wire Bonding Technology
- Finer Pitch Bonding: Machines now achieve bonds below 15µm for advanced ICs.
- Copper Wire Dominance: Rising adoption due to cost savings and performance.
- Laser-Assisted Bonding: Enhances reliability in challenging materials.
- AI & Machine Learning: Predictive maintenance and process optimization.
FAQs: Wire Bonding Machines
Q1: What’s the difference between wire bonding and flip-chip bonding?
A: Wire bonding uses wires for connections and is cost-effective, while flip-chip bonding uses solder bumps for shorter interconnects and higher performance (but at a higher cost).
Q2: Why is gold commonly used for wire bonding?
A: Gold offers excellent electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and ductility. However, copper is gaining popularity for its lower cost and superior thermal/electrical properties.
Q3: Can wire bonding handle high-power devices?
A: Yes—ribbon bonding and heavy copper wires are used for power semiconductors requiring high current capacity.
Conclusion
Wire bonding machines remain indispensable in the semiconductor industry, evolving continually to meet the demands of miniaturization and performance. From smartphones to spacecraft, this unassuming technology ensures the seamless operation of the electronics we rely on daily. As innovation accelerates, wire bonding will continue to underpin the future of microelectronics, enabling smarter, faster, and more efficient devices worldwide.
Keywords for SEO:
- Wire bonding machine
- Semiconductor packaging
- Ball bonding vs. wedge bonding
- Gold wire bonding
- Ultrasonic wire bonder
- IC assembly technology
- Copper wire bonding
- Automated wire bonding
- Semiconductor manufacturing
Internal Links (Optional to Add in CMS):
- [Advanced Semiconductor Packaging Techniques]
- [Copper vs. Gold Wire Bonding: A Comparative Guide]
- [Top 5 Trends in Semiconductor Manufacturing]
By understanding the intricacies of wire bonding machines, manufacturers and engineers can optimize their processes, reduce costs, and drive the next wave of electronic innovation. Share this guide to spread the knowledge! 🚀